Introduction : Web Development
Building websites today is not just about writing code—it’s about creating experiences that users enjoy. Web development focuses on everything that a visitor sees and interacts with on a website. From buttons, forms, and animations to layouts, colors, and navigation, frontend developers make sure websites are easy to use, look good, and perform well. Learning frontend skills helps businesses build modern, responsive, and user-friendly websites that work across devices and browsers.

What is Web Development?
Web development is the practice of building the parts of a website or web application that users interact with directly. It involves using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern frameworks to create visually appealing, responsive, and user-friendly digital experiences. The frontend is the bridge between the user and the backend, ensuring that websites look good, function smoothly, and provide seamless navigation. Frontend development is not just about coding; it combines design principles, accessibility standards, and performance optimization to ensure that websites meet both business goals and user expectations. It is a key skill for businesses and developers looking to create modern, scalable, and professional websites.
Importance in Corporate & Office Environments
Web development plays a crucial role in businesses and offices by maintaining a strong digital presence. A well-designed frontend improves user experience, supports branding, and enhances customer engagement. Teams such as marketing, HR, and operations can use frontend tools and frameworks to collaborate efficiently.
- Reduces dependency on developers for minor updates.
- Speeds up content publishing and website changes.
- Improves productivity and accuracy of displayed information.
- Supports operational efficiency for frequent updates.
Core Topics in Web Development
- UI/UX Design Principles User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) principles focus on designing websites that are intuitive, enjoyable, and easy to navigate. Good UI/UX increases engagement, reduces bounce rates, and ensures users can accomplish tasks efficiently.
- Web Accessibility (WCAG) Accessibility ensures websites are usable by everyone, including people with disabilities. Following WCAG guidelines means implementing proper contrast, keyboard navigation, alt text for images, and screen reader support. Accessible websites reach a wider audience and improve user satisfaction.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWA) PWAs combine the benefits of web and mobile apps. They are installable, work offline, and load quickly, offering app-like experiences without requiring a full mobile app. Businesses can engage users even in low-network conditions.
- Web Performance Optimization Performance optimization improves load times, responsiveness, and smooth navigation. Techniques include minimizing CSS and JS files, optimizing images, enabling caching, and using content delivery networks (CDN). Faster websites enhance user experience and improve search engine rankings.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility Websites must work consistently across all browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari) and devices. Testing and fixing compatibility issues ensures users get the same experience, no matter their platform.
- Web Animations with CSS & JS Animations make websites more engaging and interactive. CSS animations handle simple transitions, while JavaScript adds complex, dynamic interactions. Properly implemented animations improve usability and visual appeal.
- Bootstrap Bootstrap is a popular frontend framework that simplifies development with prebuilt components, responsive grids, and styling utilities. It helps create consistent and mobile-friendly layouts quickly.
- Web Security BasicsFrontend developers must understand basic security practices, including input validation, avoiding cross-site scripting (XSS), and ensuring secure data handling. Security best practices protect websites from malicious attacks and build user trust.
- Angular Routing & Navigation Angular routing allows single-page applications (SPA) to navigate smoothly between different views without full page reloads. It improves speed, user experience, and SEO when properly implemented.
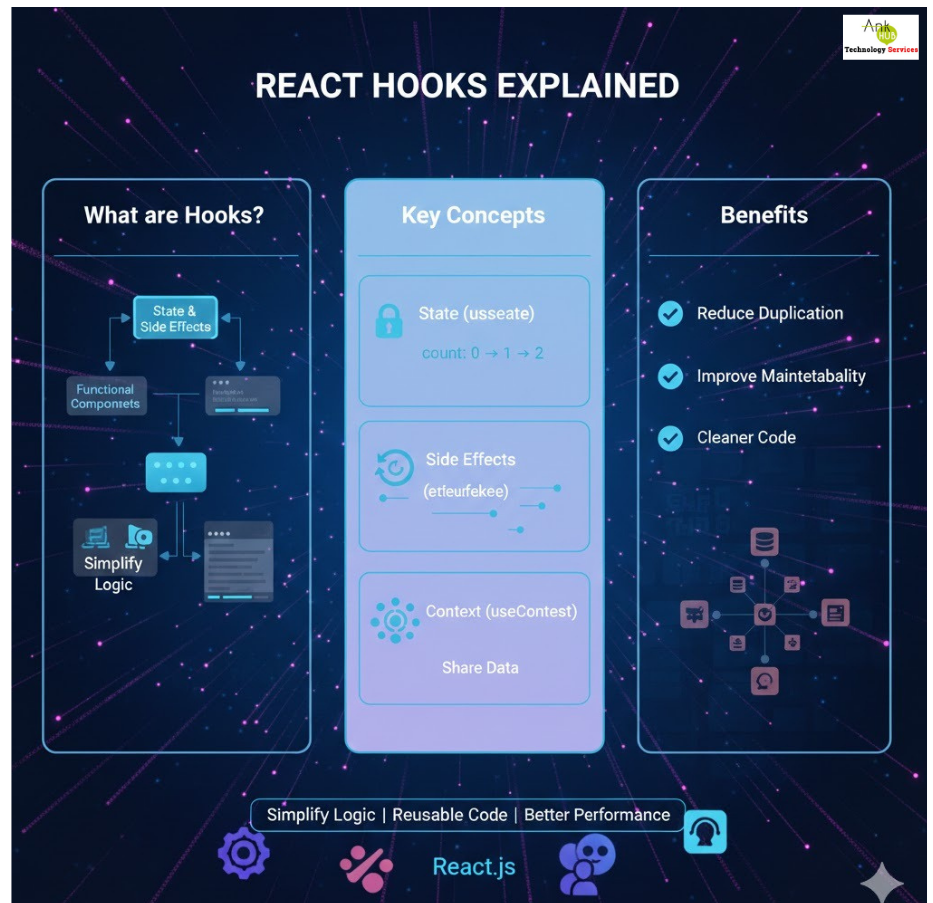
- React Hooks Explained React Hooks are functions that let developers use state and side effects in functional components. They simplify complex component logic, reduce code duplication, and improve maintainability.
- State Management in React Managing state is essential for keeping UI components synchronized with data changes. Tools like Redux or React Context allow consistent data flow across components, ensuring a reliable and predictable user experience.
Why It Matters
Web & Frontend development is essential for creating modern, responsive, and secure websites. Businesses benefit from:
- Faster development and easier maintenance
- Enhanced user engagement through intuitive design
- Improved operational efficiency for frequent updates
- Cross-platform accessibility and performance
- Scalability using frameworks like Angular and React
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between CSS Grid and Flexbox?
Grid is for complex layouts with rows and columns, while Flexbox handles one-dimensional layouts efficiently.
2. Why is web accessibility important?
Accessibility ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can access and navigate your website effectively..
3. What is a Progressive Web App (PWA)?
A PWA is a website that behaves like a mobile app, offering offline access, fast loading, and installable features.
4. How do React Hooks simplify development?
Hooks let functional components manage state and side effects easily, reducing code complexity and improving maintainability.
5. Why is web performance optimization necessary?
Faster websites provide better user experience, higher engagement, and improved search engine visibility.



