Backend development and APIs
Form the backbone of modern web applications. They handle business logic, manage databases, ensure security, and enable communication between different systems. APIs act as the bridge between the frontend and backend, allowing applications to exchange data efficiently and securely. Here’s a deeper look into each major backend topic:
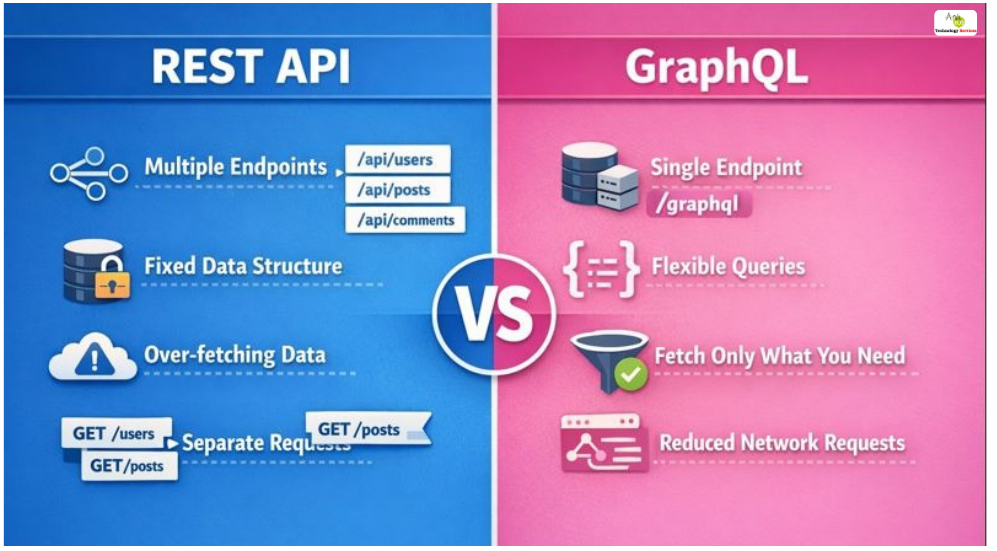
REST API vs GraphQL
REST APIs use predefined endpoints and HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to fetch or modify data. They are simple, widely adopted, and excellent for standard CRUD operations. GraphQL, on the other hand, allows clients to request exactly the data they need, avoiding over-fetching or under-fetching. It also supports real-time updates via subscriptions, making it ideal for modern, data-heavy applications. Choosing between REST and GraphQL depends on project complexity, client requirements, and scalability needs.
API Security
APIs are entry points to your backend, making security crucial. Common techniques include:
1. HTTPS for encrypted data transmission.
2. Authentication tokens (JWT, API keys).
3. Rate limiting to prevent abuse
4. Input validation to avoid SQL injection and other attacks
5. Logging and monitoring for unusual activity, Securing APIs not only protects sensitive data but also builds user trust.
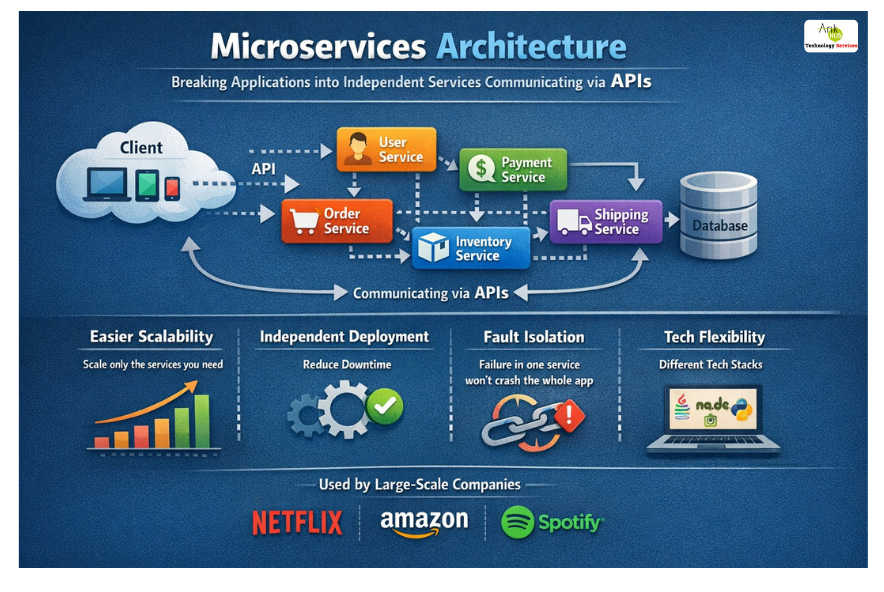
Microservices Architecture
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing allows developers to run code without managing infrastructure. Functions are deployed on cloud providers (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions). Benefits include:
1. Automatic scaling.
2. Reduced operational overhead.
3. Cost-efficiency (pay only for compute time used).
4. Rapid development and deployment, Serverless is excellent for event-driven applications, APIs, and small-to-medium workloads.
Authentication & Authorization
Authentication confirms the identity of a user (login credentials, OAuth, SSO). Authorization controls what actions an authenticated user can perform. Best practices include:
1. Role-based access control (RBAC).
2. Multi-factor authentication (MFA).
3. Secure token management Strong authentication and authorization are vital for protecting sensitive user data and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Web Sockets
WebSockets enable persistent, full-duplex communication between client and server, unlike HTTP which is request-response. Use cases include:
1. Real-time chat apps.
2. Live notifications and dashboards.
3. Online gaming.
4. Collaborative document. editing WebSockets help create dynamic, real-time user experiences.

Caching Techniques
Caching improves performance by storing frequently accessed data in memory or on edge servers. Common methods:
1 In-memory caches (Redis, Memcached).
2. Browser or CDN caching for static assets.
3. Query result caching for databases Effective caching reduces database load, decreases latency, and improves scalability.
Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming requests across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability. Types include:
1. Hardware vs software load balancers.
2. Round-robin, least. connections, IP hash methods Benefits:
3. Prevents server overload.
4. Reduces latency.
5. Improves fault tolerance Load balancing is critical for handling traffic spikes and providing a consistent user experience.
OAuth 2.0
OAuth 2.0 is an industry-standard authorization framework that allows secure access to APIs without sharing passwords. Key features:
1. Access delegation for third-party apps.
2. Token-based authorization (short-lived access tokens).
3. Supports social logins (Google, Facebook).
4. Scalable for multiple devices and applications It simplifies authentication while maintaining security across applications.
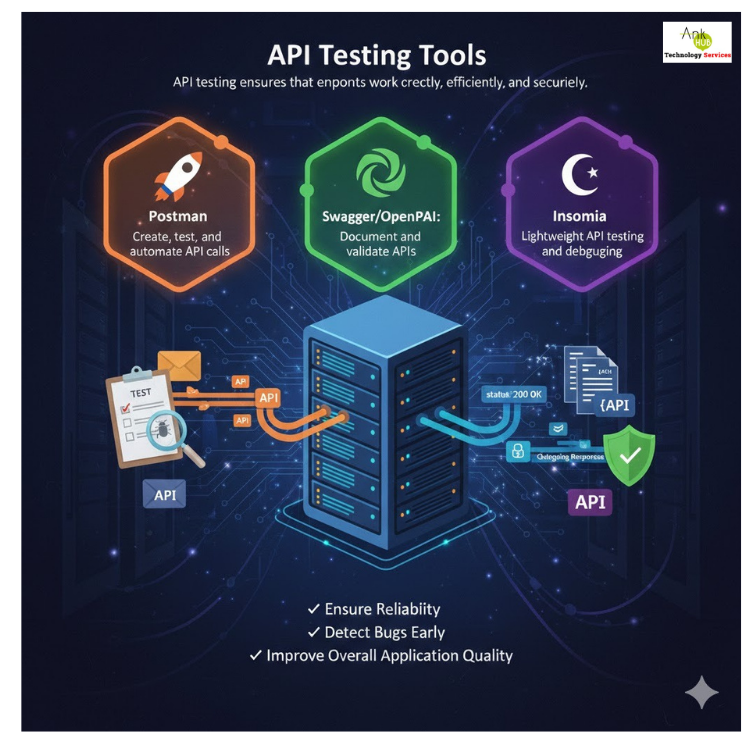
API Testing Tools
API testing ensures that endpoints work correctly, efficiently, and securely. Popular tools include:
1. Postman: Create, test, and automate API calls.
2.Swagger/OpenAPI: Document and validate APIs.
3.Insomnia: Lightweight API testing and debugging Testing APIs ensures reliability, detects bugs early, and improves overall application quality.